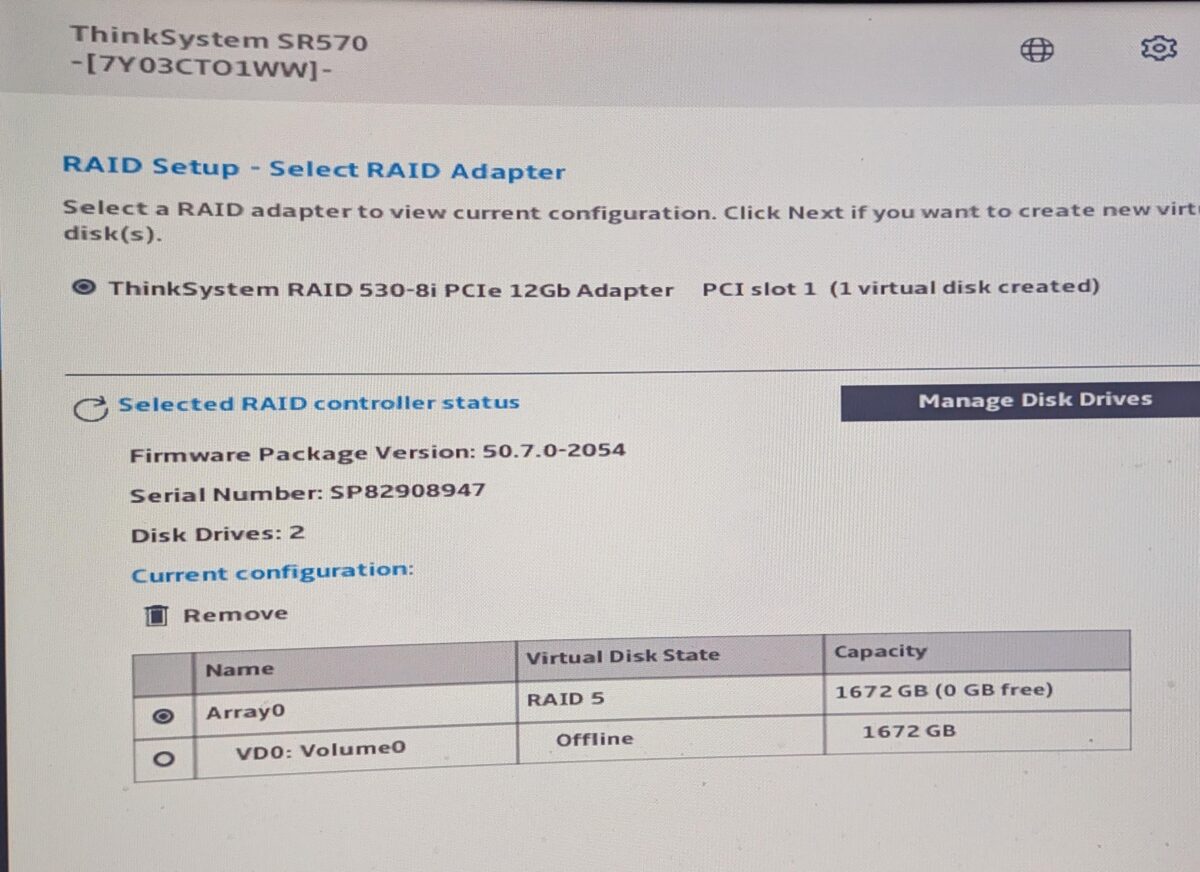
The Dell PERC HBA330/530-8i PCIe 12Gb RAID controller supports SAS and SATA drives — both types.
Here’s the breakdown:
✅ Supported Drives:
| Drive Type | Supported? | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) | ✅ Yes | Full 12Gbps support |
| SATA (Serial ATA) | ✅ Yes | Up to 6Gbps (limited by SATA standard) |
💡 Key Details:
- “12Gb” refers to SAS speed (SATA maxes out at 6Gbps).
- The controller is backward-compatible with 6Gb SAS and SATA III.
- “8i” = 8 internal ports via 2 Mini-SAS HD (SFF-8643) connectors.
- Typically used in Dell PowerEdge servers.
🧠 Use Case Summary:
| You want to use… | Works? | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| 12Gbps SAS SSDs | ✅ Yes | Max performance |
| 6Gbps SATA SSDs | ✅ Yes | Lower speed, still compatible |
| SAS HDDs | ✅ Yes | Common in enterprise setups |
| SATA HDDs | ✅ Yes | Cheaper but slower |
🛠 Requirements:
- Drives must connect via a backplane or breakout cables (SFF-8643 to 4x SATA or SAS).
- You’ll need appropriate cables to match drive connectors.
🚫 What It Doesn’t Support:
- NVMe drives
- IDE, M.2 SATA directly (unless adapted externally, not recommended)
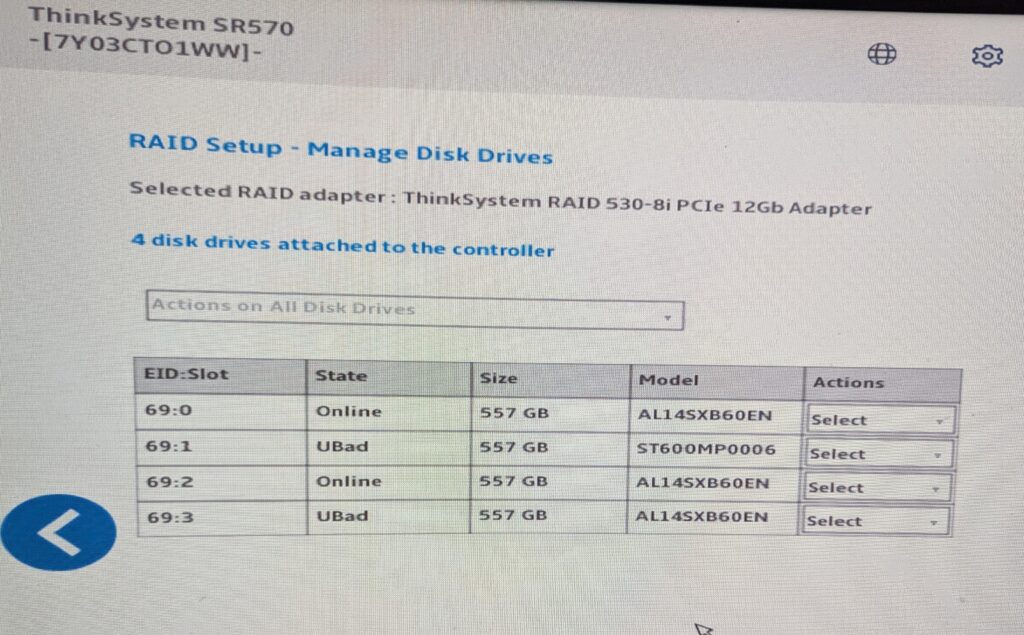
RAID mode setup vs. HBA mode
very important distinction when working with controllers like the Dell PERC 530-8i or similar RAID/HBA cards.
Let’s break down RAID mode vs. HBA mode, both in theory and in practice:
⚙️ What’s the Difference?
| Feature | RAID Mode (aka “RAID BIOS/Controller Mode”) | HBA Mode (Host Bus Adapter / IT Mode) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Controller manages virtual disks using RAID | Passes drives directly to OS/host |
| Visibility | OS sees RAID volumes only | OS sees individual drives |
| Performance | Slightly more overhead (depends on RAID level) | Often lower latency & full OS control |
| Use case | Best for redundancy (RAID 1, 5, 10, etc.) | Best for software RAID, ZFS, or direct disk access |
| Hot-swap support | Yes (with proper RAID config) | Yes (depends on OS support) |
| Recovery | Replacing failed disk requires rebuilding array | Disk is visible — just replace and remount |
| Popular in | Enterprise servers, VMware ESXi, Windows Server | FreeNAS, TrueNAS, ZFS, Linux mdadm, Proxmox |
🔍 RAID Mode — What Happens?
In RAID mode, the controller:
- Hides the physical drives from the OS.
- Creates virtual drives (“logical volumes”) from RAID arrays.
- You configure arrays (RAID 0/1/5/6/10) via:
- Controller BIOS
- Dell’s OpenManage / PERC utility
- You can’t access individual drives — only the virtual RAID array.
Example:
If you configure 4 drives in RAID 10 → your OS sees 1 virtual disk, not 4.
🔌 HBA Mode (aka IT Mode or JBOD Mode)
- HBA mode tells the controller to act like a dumb pass-through.
- No RAID logic, no metadata — just exposes raw disks directly to the OS.
- Your operating system or hypervisor can handle the RAID/software volume (ZFS, Windows Storage Spaces, etc.).
Example:
FreeNAS/TrueNAS prefers HBA mode so it can handle ZFS checksums and disk integrity.
🧰 Which One Should You Use?
| You should use… | If you: |
|---|---|
| RAID mode | Want simple redundancy, are using Windows/Linux without software RAID, or prefer hardware-managed arrays. |
| HBA mode | Want ZFS, Proxmox, TrueNAS, or need individual disk access for backup, monitoring, or flexibility. |
🛠 How to Switch Modes (Dell PERC 530-8i Example)
1. RAID Mode:
- Default mode for Dell PERC.
- Enter controller BIOS during boot (
Ctrl+R) - Configure Virtual Disk (RAID 0/1/5/10, etc.)
2. HBA/IT Mode:
- Requires flashing firmware to IT-mode version (not officially supported by Dell).
- Some PERC models (like H310, H330) can be cross-flashed to LSI IT firmware.
- ⚠️ Flashing voids warranty and requires care.
🧠 Summary
| RAID Mode | HBA Mode |
|---|---|
| Great for plug-and-play redundancy | Great for flexibility and software-defined storage |
| OS sees only RAID volumes | OS sees all disks individually |
| Good for VMware/Windows | Ideal for ZFS/Linux mdadm/Proxmox |